What is a Digital Credential? Understanding Its Importance to Enhance Your Cybersecurity Awareness!
2024/10/14
What is a digital credential? Do you know that using digital credentials is closely related to daily life? This article will explain the definition, content, and acquisition methods of digital credentials. Further, we will discuss how to verify digital certificates through digital signatures. To learn more about professional digital credential services, continue reading!
Table of contents
I. What is a digital credential? How to obtain it?
- A. The basic concept of digital credential
- B. What does digital credential include? Clarify the difference between the public key and the private key credential!
- C. How to obtain a digital certificate?
II. Where Can Digital Certificate Be Applied? Discover Common Uses of Digital Certificates!
III. How to ensure the security of digital credentials? Introduction to the 2 major methods of digital verification
- A. Digital signature
- B. Timestamp
- C. Supplementary explanation: Even with a digital signature, are digital certificates still risky?
IV. Discover the Best Digital Credential Services with Turing Certs
I. What is a digital credential? How to obtain it?
In the digital age, the Internet has become an integral part of our personal and professional lives. With an overwhelming amount of digital information constantly evolving, it is crucial to ensure the safety and reliability of this data. One effective method to achieve this is through the use of digital credentials, which provide a secure and trustworthy verification process for information.
A. The basic concept of digital credential
Before introducing “digital certificates”, let’s talk about what “certificates” are.
In daily life, every document that can be used as proof is a certificate. Typical examples of such documents include ID cards, driver’s licenses, certificates of degree, physical examination reports, and employment contracts.
With a clear understanding of the concept of a certificate, the definition of a “digital certificate” becomes more straightforward. A digital certificate is a digital version of an identity proof. It can verify the identity of the information owner and confirm their qualifications for information review and access. In this scenario, network information management will remain secure and out of the hands of unauthorized individuals.
The term “Digital Credential” originally referred to “all identity authentication information” of computer users. However, in Taiwan, the term “Digital Certificate” is limited to information technology and is understood to mean “certificate at the network level.” This may contribute to the perception that Digital Certificates are abstract and difficult to understand. However, the digital certificate can just easily regarded as a form of online identity authentication.
B. What does digital credential include? Clarify the difference between the public key and the private key credential!
The principle of the digital certificate is to utilize public key cryptography to encrypt (similar to “locking”) the information with a “digital key”. Thus, the information can only be read by the specified person, and the specified person needs to decrypt (similar to ‘ unlocking ’) to check the information. Consequently, digital certificates are also called Public Key Certificates.
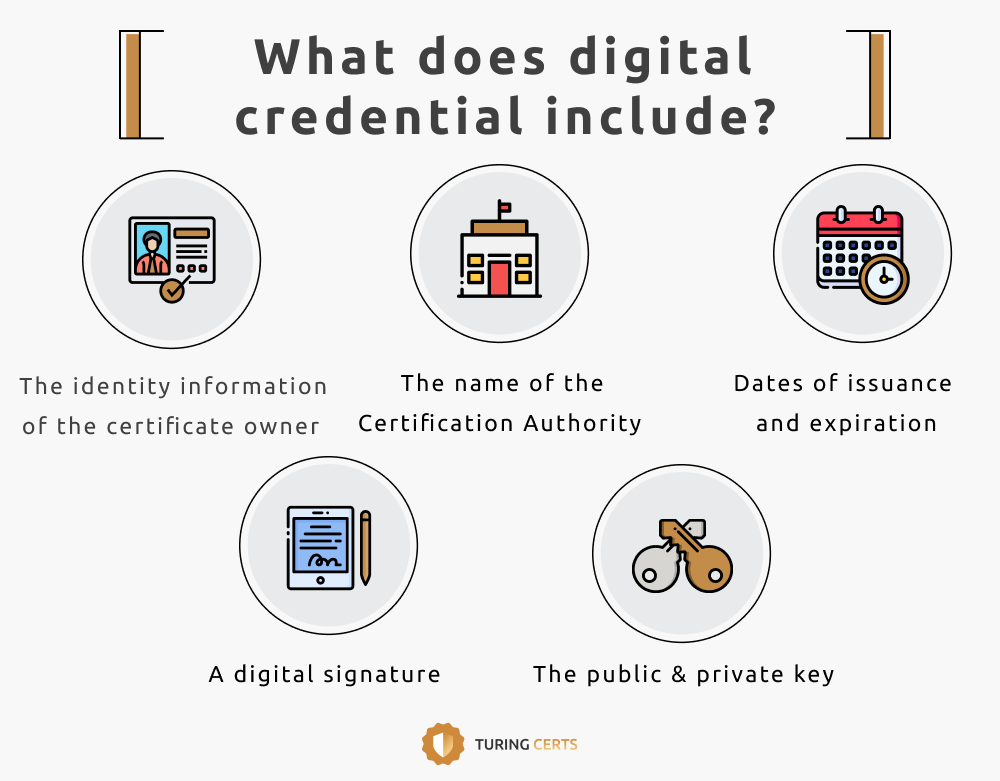
A complete digital certificate includes
- The name and identity information of the certificate owner.
- The name of the Certification Authority that issued the certificate.
- The issuance and expiration dates of the certificate.
- A digital signature.
- A pair of keys
- The public key can encrypt the digital information and verify the digital signature.
- The private key can decrypt the digital information and sign the digital signature.
There are many common types of digital certificates, for instance, citizen digital certificates, server certificates, Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates, Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates, and so on.
C. How to obtain a digital certificate?
a. Certification Authority (CA)
Just like ordinary credentials are issued by credible institutions, digital certificates also have specialized issuing units.
Digital certificates are issued by the Certification Authority (CA). This center can provide the generation, issuance, verification, and management services of digital certificates. Therefore, it must be an authoritative third-party organization responsible for ensuring the trustworthiness of digital certificates.
The Certification Authority (CA) plays a very important role in digital security management. In addition to being an independent third-party organization, it can also be connected with other subordinate organizations.
The Certification Authority will issue a Root Certificate, which is used to verify other lower-level certificates and issue an Intermediate Certificate. Finally, the Intermediate Certificate will issue an End Entity Certificate to the user. Establish layers of digital security protection to form a certificate chain (also called a trust chain).
For example, Taiwan’s government agencies have such a chain of credentials.
The Government Certification Authority (GRCA) established by the Ministry of Digital Affairs issues Government Root credentials and can certify intermediate certificates of lower-level agencies. For example, an intermediate certificate issued by the Ministry of Interior Certificate Authority (MOICA). This intermediate certificate can be re-issued terminal credentials, a citizen digital certificate, to the public. So that people can obtain the government’s digital services through citizen digital certificates, and conduct online tax filing, household registration, etc.
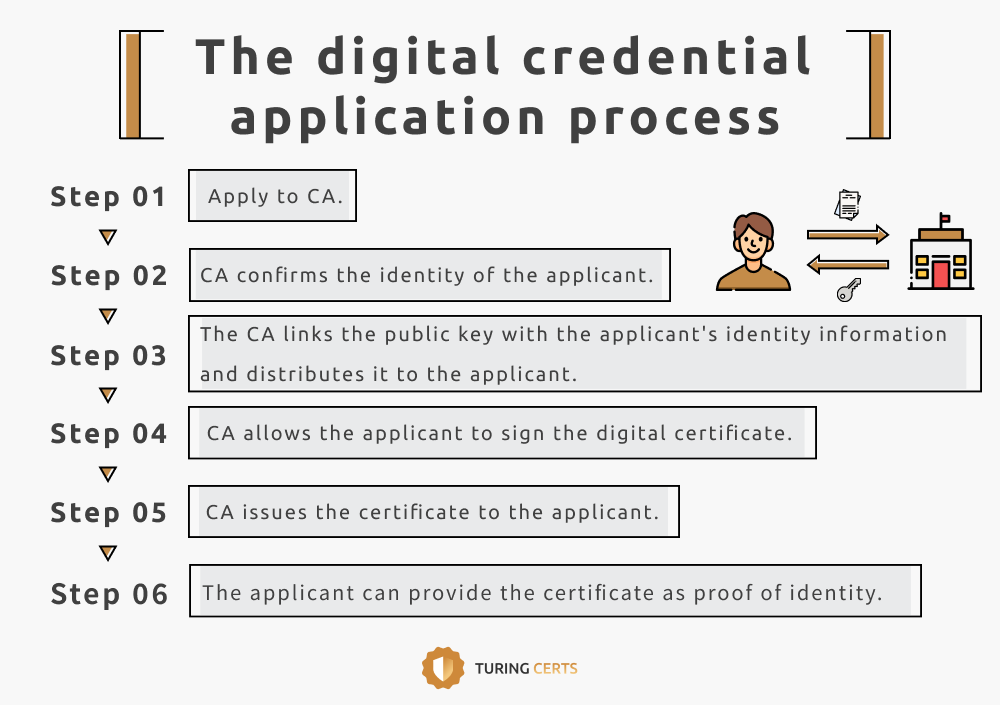
So, how do we apply for and obtain digital certificates from the Certificate Authority? Let’s take a look at the digital credential application process!
STEP 1. Apply to CA.
STEP 2. CA confirms the identity of the applicant.
STEP 3. The CA links the public key with the applicant’s identity information and distributes it to the applicant.
STEP 4. CA allows the applicant to sign the digital certificate so that others cannot forge or tamper with it.
STEP 5. CA issues the certificate to the applicant.
STEP 6. The applicant can provide the certificate as proof of identity or establish encrypted confidential communication.
b. Self-signed certificate
We can still obtain digital certificates even if they are not issued through the CA. Certificates that are not obtained through the CA are called “Self-signed Certificates”.
Self-signed Certificate is a digital certificate that is self-signed through a personal private key. It has no cost and does not require a third-party certification. Its encryption function is the same as that of the digital certificate issued by the CA.
However, self-signed certificates are not trustworthy and may be attacked by unknown parties.
The few self-signed certificates with credibility are only Root Certificates. This is because the root certificate is the starting point of the certificate chain (trust chain). Therefore, the root certificate is usually trusted by most terminal certificate users.
II. Where Can Digital Certificate Be Applied? Discover Common Uses of Digital Certificates!
We have already learned that a digital certificate is a method of online identity verification. This raises the question of where digital certificates are most applicable.
Digital certificates have been an integral part of our lives for an extended period, much like physical certificates and licenses. In essence, all digitalized documents can be considered as digital certificates, including the most commonly used QR Code scanning code. The technology behind the QR Code is also a digital certificate, as it can verify your mobile device by scanning the code.
Take Turing Certs as an example. It has been applied across 12 industries and 25 types of credentials!
| Industries | Government Agencies, International Organizations, ESG, Healthcare, Education, Real Estate, Art, Funerals, Agriculture, Automobiles, Pets, and Sports. |
| Types of Certificates | Certificate of Award, Certificate of Training Completion, Certificate of Attendance, Certificate of Proficiency, Certificate of Volunteer, Certificate of Degree, Certificate of Internship, Certificate of Supervisor, Certificate of Professor, Certificate of Membership, Certificate of Appreciation, Transcript, Certificate of Transaction, Certificate of Artwork, Certificate of Artwork Collection, Certificate of Construction, Certificate of Liquor, Certificate of Agricultural Traceability, Carbon Footprint Certificate, Certificate of Corporate ESG, Certificate of Corporate Recognition, Certificate of Automobile Maintenance, Report of Physical Examination, Certificate of Relative Memorial, Certificate of Qualified Business Owner, etc. |
Turing Certs can offer you different user scenarios of digital credentials!
💡 Additional Tips:
In the early days, when computers were first invented, digital credentials were essential for ensuring the quality of machine connections and protecting against malicious attacks as devices were first connected to networks.
In today’s network infrastructure, it is still necessary to verify that the other party has the corresponding credentials to ensure secure communication and interaction. As an illustration, a considerable amount of digital certificate encryption technology is utilized in the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), program code, and software employed by browsers to connect to web pages.
III. How to ensure the security of digital credentials? Introduction to the 2 major methods of digital verification
In addition to relying on trust in the CA, is there any other way to ensure the security of digital credentials? Among digital certificates, there are digital signatures such as “digital signature” and “timestamp” to further confirm that the source of the digital certificate is safe and reliable.
A. Digital signature
Physical certificates can be forged or tampered with. How can digital certificates meet the same level of authenticity?
To guarantee the legitimacy of a certificate, a variety of anti-counterfeit measures are employed in everyday practice. These include the use of seal stamps, sealing wax, watermarks, autographed signatures, company seals, and other techniques to substantiate the credibility of the certificate’s source. For instance, when Party B signs the contract, the contract must bear Party A’s seal stamp and autograph, which allows Party B to ascertain that the contract is genuine and has not been altered or forged.
A digital signature is also an anti-forgery method of a digital certificate. If a digital certificate is viewed as an official document, the digital signature can be seen as the sealing wax or seal stamp on the document.
The digital signature is based on public key cryptography, which is used to verify the certificate through asymmetric encryption. The original owner of the digital certificate uses the private key to sign the certificate (similar to a signature and seal) and publishes the public key so that other parties can verify the certificate.
In the circumstance of establishing a chain of credentials (a chain of trust), the digital signature can be employed to confirm that the terminal certificate originates from a superior organization or a root certificate/intermediate certificate, thus providing further verification of the security of the encrypted information.
💡Additional Tips: What is “asymmetric encryption”?
The key used for encryption and decryption is not the same. Rather, it is a pair of different public keys and private keys, which is why this method is known as asymmetric encryption.
B. Timestamp
In addition to digital signatures, it is important to understand the basic concept of a timestamp.
A timestamp is a digital signature formed via an encrypted algorithm through a time server. It allows digital certificates to include a credible date and time of signing, enhancing the credibility of the digital signature. A timestamp effectively verifies the time point of signing and execution of the digital certificate, thereby providing greater protection for the digital signature.
C. Supplementary explanation: Even with a digital signature, are digital certificates still potentially risky?
It is important to note that even if a digital certificate includes a signed digital signature, there may still be risks involved. As digital data, it will certainly be exposed to information cybersecurity risks. Therefore, enterprises must be more careful in the management of digital data and it is crucial to choose a reliable CA.
Once a digital signature has been obtained, potential risks associated with the digital certificate may still exist, particularly in the following areas:
- Legality: While a digital signature can verify the legitimacy of a certificate’s source, it’s important to note that regulatory restrictions may vary by country, impacting the scope of its use.
- Privacy: A digital signature is based on asymmetric encryption technology. While a digital signature can confirm the authenticity of the certificate’s origin, it does not guarantee the transmission of information has not been hacked or contains any malicious content.
- Content Accuracy: A digital signature can guarantee the legitimacy of the certificate’s source, yet the recipient is uncertain about the contents of the digital certificate. Therefore, if an individual with malicious intent gains access to the key, they can impersonate the original certificate owner and send messages on the owner’s behalf.
IV. Discover the Best Digital Credential Services with Turing Certs
Turing Space is a TrustTech startup founded by Jeff Hu in 2020, dedicating to addressing the complexity of certifications among industries worldwide. We build up a borderless digital trust network with blockchain technology and cybersecurity, advancing global digital transformation, aiming to become the cornerstone of international trust transmission.
What digital credential services can Turing Certs provide you?
✅ Digital credential creation
✅ Large-quantity, quick credential issuance
✅ Effective digital credential and resource management
✅ One-stop rental management with reasonable prices
✅ Verifiable information and immutable blockchain records
✅ Strictly verified digital credentials for enhanced information security
✅Provide real-person customer service support so that even novices in digital tools can adapt quickly
![]() Media Contact|[email protected]
Media Contact|[email protected]