What is a Digital Signature? Secure Your Information with Encryption & a 6-Step Signing Process
2024/6/30
In the digital era, securing electronic documents and transactions is crucial to prevent fraud and unauthorized access. Digital signatures are cryptographic security measures that authenticate the identity of the signer and ensure the integrity of documents.
Table of contents
I. What is a Digital Signature? Is it Legally Recognized?
- A. Definition of a Digital Signature
- B. How Digital Signatures Work
- C. 3 Key Legal Elements of a Digital Signature
II. Digital vs. Electronic Signatures: What’s the Difference?
III. How Do Digital Signatures Work? Encryption & Signing Process
- A. Introduction to the principles of digital signature
- B. Step-by-Step Guide to Apply a Digital Signature
IV. Turing Certs: The Most Secure Digital Signature Solution
I. What is a Digital Signature? Is it Legally Recognized?
A. Definition of a Digital Signature
Digital Signature is an anti-counterfeiting method that can verify the authenticity of digital credentials such as electronic documents and electronic certificates.
According to Article 2, Item 3 of Taiwan’s “Electronic Signatures Act” by the Ministry of Digital Affairs, a “digital signature” refers to a type of electronic signature created using mathematical algorithms or other cryptographic methods to generate a specific length of digital data encrypted with the signatory’s private key. It can be verified using a public key and is supported by a certificate issued by a certification authority.
To simplify, the digital signature is a way of signing e-documents. It is encrypted with the “private key” that belongs to the document owner. When others receive a digitally signed document, they can use the ‘public key’ to verify the signature. If the verification is correct, it can prove that the original owner truly signed the document and that the contents have not been tampered with or forged.
If you see an e-document as an official printed letter, a digital signature is a seal that can prove the letter’s authenticity.
B. How Digital Signatures Work
There are 3 main functions of digital signature:
- Ensure the identity of the signer: Digital signatures can authenticate the identity of the signer to ensure that the signer of an e-document is the actual owner or authorizer of the document.
- Keep the security and integrity of document content: Digital signatures can maintain the integrity of e–document content and prevent it from being tampered with or omitted.
- Avoid contract disputes: A legally valid digital signature can protect the rights and interests of both parties and prevent either party from repudiating the contract.
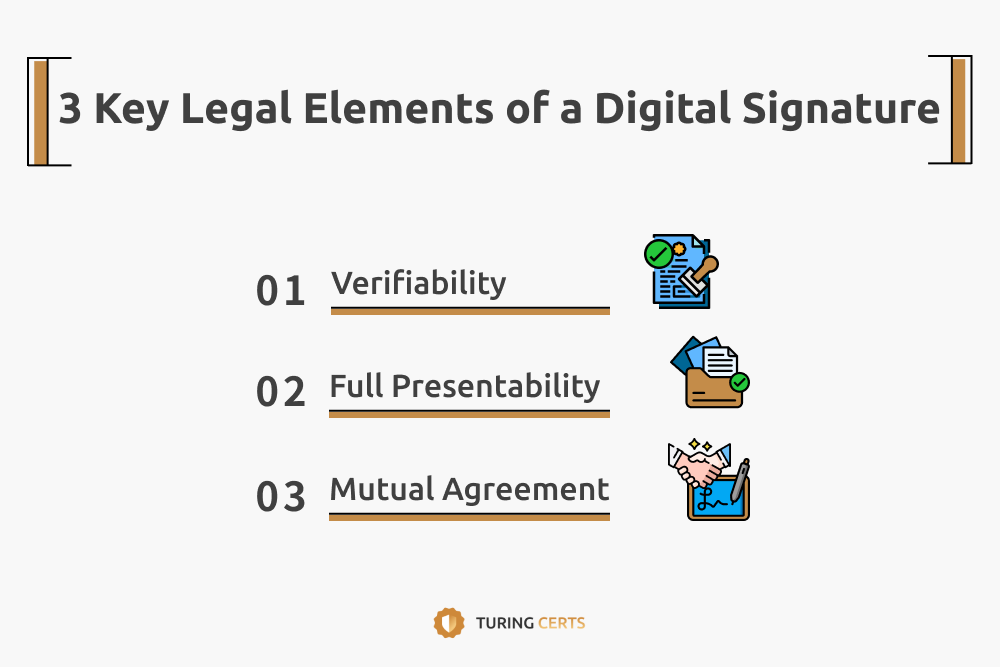
C. 3 Key Legal Elements of a Digital Signature
To be legally valid, a digital signature must meet three criteria:
- Verifiability – Must be issued by a recognized Certification Authority (CA).
- Full Presentability – Must be readable and accessible in any format or device.
- Mutual Agreement – Both parties must consent to digitally sign the document.
II. Digital vs. Electronic Signatures: What’s the Difference?
The most common way to sign a document is to sign it with a physical handwritten signature. However, paper documents are not only easily damaged and not conducive to archiving, but also have low security. Therefore, with the development of digital documents, handwritten signatures have gradually been transformed into electronic signatures and digital signatures.
Digital signature is a type of electronic signature, but the two have different meanings.
The electronic signature covers a wide range, as long as it is in electronic form, i.e. the signatures generated through digitizing can be considered as electronic signatures. Common forms include text, images, symbols, etc. Scanned documents of handwritten signatures are also counted as electronic signatures.
Digital signatures refer specifically to the signature generated by encryption algorithm technology.
The biggest difference between digital and electronic signatures is security. Digital signatures use algorithms, encryption technology, and third-party certification authorities to enhance security and credibility, while electronic signatures lack the guarantee of these certificates.
📌Table of Digital and Electronic Signature Differences
| Digital signature | Electronic signature | |
| Security | Highest | Lower |
| Verification method | Key encryption technology | Electronic format |
| Application Scenarios | E-commerce, financial operations, e-certificates, government documents, etc. | Emails, contracts, agreements, etc. |
III. How Do Digital Signatures Work? Encryption & Signing Process
A. Introduction to the principles of digital signature
a. Encryption Methods: Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Cryptography
Digital signatures and digital documents are based on the same encryption principle, but the execution method is slightly different.
Digital signature uses asymmetric cryptography to sign documents with a private key and verify signatures with a public key. Besides digital signature, asymmetric cryptography can also be applied to digital credentials, which encrypts the document with the public key (lock) and decrypts the document with the private key (unlock).
- Symmetric Encryption: One lock matches one key. The key for encryption and decryption is the same. Thus, if you lock with key A, you can only open with key A.
- Asymmetric Encryption: The key that encrypts and decrypts is not the same, but a pair of different public and private keys. Use public key A to lock, but use private key B to open. The private key is not publicly available, so it can be used to decrypt or sign files.
b. RSA
RSA is one of the most widely used asymmetric encryption algorithms for digital signatures, secure email, and online banking. It was developed at MIT in 1977 and remains a critical security standard.
B. Step-by-Step Guide to Apply a Digital Signature
a. How to Obtain & Use a Digital Signature
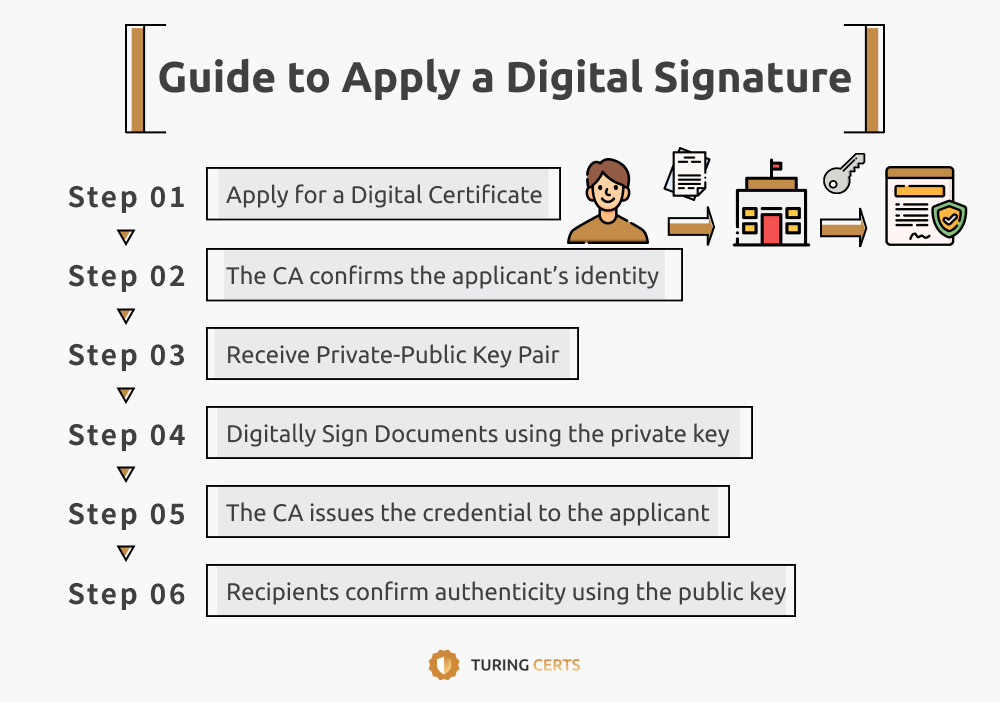
Follow these six essential steps to securely sign digital documents:
STEP 1. Apply for a Digital Certificate from a Certification Authority (CA).
STEP 2. The CA confirms the applicant’s identity.
STEP 3. Receive Your Private-Public Key Pair linked to your verified identity.
STEP 4. Digitally Sign Documents using the private key.
STEP 5. The CA issues the credential to the applicant.
STEP 6. Recipients confirm authenticity using the public key.
b. Security Precautions for Digital Signatures
Even the most secure encryption methods are vulnerable to cyber threats. Here’s how to safeguard your digitally signed documents:
- Use a trusted Certification Authority (CA) for issuing digital certificates.
- Ensure public key & identity binding to prevent unauthorized access.
- Store private keys securely to prevent cyberattacks.
- Verify signed documents before accepting them to avoid fraudulent transactions.
IV. Turing Certs: The Most Secure Digital Signature Solution
Turing Space is a TrustTech startup founded by Jeff Hu in 2020, dedicating to addressing the complexity of certifications among industries worldwide. We build up a borderless digital trust network with blockchain technology, advancing global digital transformation, aiming to become the cornerstone of international trust transmission.
With Turing Certs, you can gain a variety of e-document services:
✅Large-quantity, quick credential creation and issuance
✅Sign digital credentials
✅Effectively manage digital credentials
✅One-stop rental management with reasonable prices
✅ Verifiable information and immutable blockchain records
✅ Strictly verified digital credentials for enhanced information security
✅Provide real-person customer service support so that even novices in digital tools can adapt quickly
![]() Media Contact|[email protected]
Media Contact|[email protected]