What is InfoSec? Master the 3 Core Elements, 8 Major Threats, and Best Protection Strategies!
2024/6/30
What is information security (InfoSec)? This article will define InfoSec and introduce the three elements of InfoSec, CIA. Then tell how to plan an enterprise InfoSec strategy in 5 steps. Moreover, it will explain the 5 major infoSec protection mechanisms and 8 major InfoSec attack methods in depth. Finally, offer the best InfoSec solution!
Table of content
I. What is Information Security? The CIA Triad Explained
II. Advanced InfoSec Strategies for Enterprises
III. Five Types of Information Security to Strengthen Defense
- A. Cybersecurity
- B. System Security
- C. Application Security
- D. Cloud Security
- E. Data Encryption & Authentication
IV. Cyber Threats & InfoSec Protection Measures
V. Turing Certs, the best solution to information security issues!
I. What is Information Security? The CIA Triad Explained
A. Definition of InfoSec
Information security (InfoSec) refers to the mechanism and technology that help protect those sensitive assets. In the digital era, personal and business information is commonly uploaded to computers or backed up to the cloud. If the information is not properly and securely managed, malicious hackers can easily access, manipulate, and steal it. As a result, InfoSec becomes important.
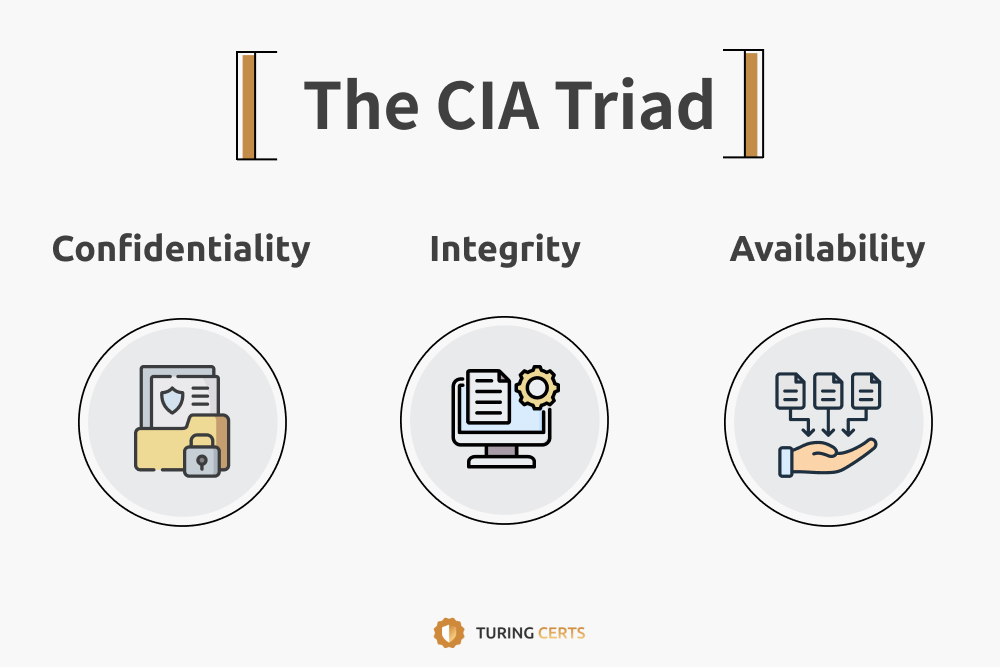
B. The Three Core Elements of InfoSec: CIA
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) first defined the three elements of information security in 1977: confidentiality, integrity, and availability, also known as #TheCIATriad.
Digital information management can only reach the foundation of information security if it meets these three key elements:
a. Confidentiality
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive digital information remains private and accessible only to authorized users. This prevents unauthorized individuals from viewing, modifying, or leaking data.
b. Integrity
Integrity guarantees that data remains complete, accurate, and tamper-proof, preventing unauthorized alterations or corruption.
c. Availability
Availability means that authorized users must be able to access and use data whenever needed, without delays or disruptions.
II. Advanced InfoSec Strategies for Enterprises
A. InfoSec Maturity Levels
Organizations can classify their information security risks into five levels:
| 分級 | 解說 | 舉例 |
| Level A | The business involves sensitive matters, including state confidentiality, national defense, national infrastructure, and public medical centers. | Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of National Defense, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, etc. |
| Level B | The business involves municipal governments, public regional hospitals, and so on. | Taipei City Government,Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Central Bank, etc. |
| Level C | The business involves county and municipal governments, public regional hospitals, etc. | Hsinchu County Government, Academia Sinica,Industrial Technology Research Institute, etc. |
| Level D | The agency is independently responsible for managing digital information circulation, but does not maintain or operate the information communication system that it has set up and developed itself or outsourced. | Local police station, fire brigade, etc. |
| Level E | Organizations are not required to maintain their own information system hosts, and they may not have any information business needs, but they are still obligated to take measures to protect their information security. | Private schools,large corporation, SMEs, etc. |
B. 5 Steps to Implement Enterprise InfoSec Policies
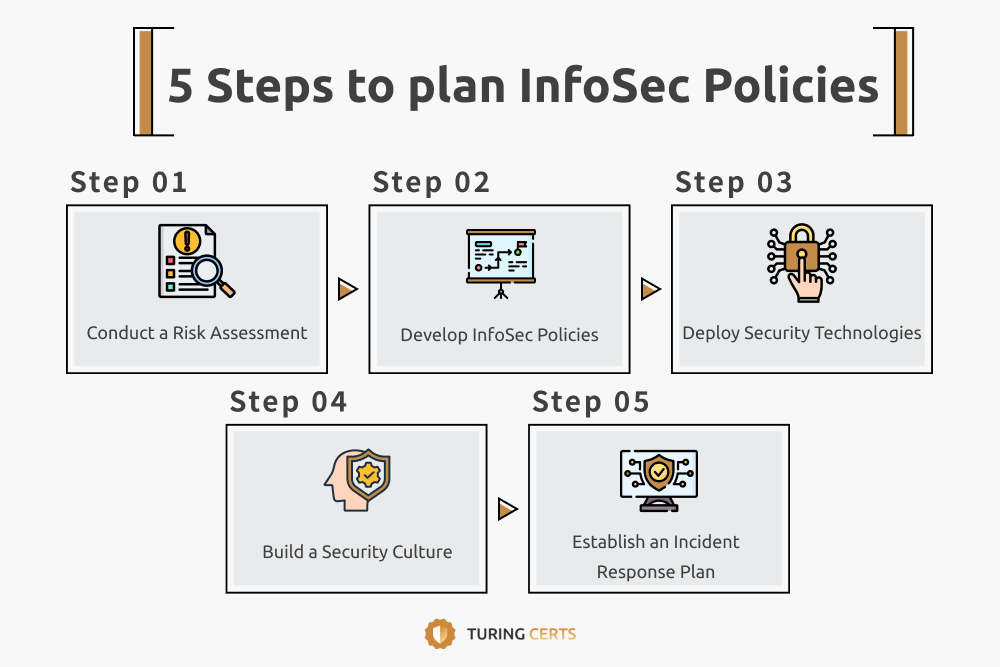
Enterprises and organizations can grade their information security from A to E and follow the following 5 steps to plan their information security strategy:
Step 1: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Identify data vulnerabilities based on classification levels.
Step 2: Develop InfoSec Policies
Establish security standards and define digital access regulations.
Step 3: Deploy Security Technologies
Implement firewalls, credential management, and identity verification tools.
Step 4: Build a Security Culture
Conduct cybersecurity training to prevent human errors.
Step 5: Establish an Incident Response Plan
Define procedures to mitigate data breaches, ransomware, and hacking attacks.
III. Five Types of Information Security to Strengthen Defense
The scope of information security is quite broad and not limited to general digital information management. Information security can be divided into the following five categories according to the different application scenarios of digital technology:
A. Cybersecurity
Protects networks, servers, browsers, and web applications from unauthorized access, hacking, and malware.
B. System Security
Secures operating systems and enterprise software by patching vulnerabilities, preventing DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks, and securing authentication mechanisms.
C. Application Security
Focuses on securing apps and software by implementing penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and encryption techniques.
D. Cloud Security
Ensures data privacy in cloud environments, preventing data leaks and unauthorized third-party access.
E. Data Encryption & Authentication
Uses blockchain-based credentialing, digital signatures, and cryptographic key management to secure identity verification and prevent data forgery.
IV. Cyber Threats & InfoSec Protection Measures
A. 8 Common Cyber Threats
It is crucial to understand the most common information security vulnerabilities and hacker attack methods. By recognizing these methods, we can enhance our information security awareness and minimize information security risks.
💀Phishing
To trick users into clicking on fake URLs and web pages to achieve certain malicious purposes, the attacker typically pretends to be an official organization or company and then sends the link via email or message.
💀Malware
Most malware contains malicious content, such as computer viruses and Trojan horses.As long as the user installs and starts the software, it will cause computer paralysis.Some attackers will use this to lock the user’s computer information and threaten the user to pay through the Internet. This software is called “Ransomware.”
💀Decentralized Denialing (DDoS)
The attacker will send a large number of data requests to prevent the server from functioning properly, thereby paralyzing the website and preventing users from entering or browsing normally.This attack method is called DDoS.
💀Zero-Day Vulnerability
Zero-day vulnerabilities are attacks carried out when a system has vulnerabilities but hasn’t been patched yet. This often occurs when the system is still under maintenance.
💀Password Attack
Password attacks are a common information security threat. Attackers steal or crack user passwords using various methods to achieve a malicious purpose.
💀Social Engineering Attack
Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology and weaknesses to coerce information users into leaking confidential information, ultimately breaching organizations’ and enterprises’ information security protections.
💀SQL Injection Attack (SQL Injection)
The attacker will insert SQL code containing malicious instructions into the input string. The system’s or application’s lack of design will cause it to be unable to detect problems in the characters, resulting in the malicious instructions being directly executed. This will paralyze the system or provide an opportunity to steal confidential information.
💀Cross-site Scripting Attack (XSS)
The attacker will inject malicious (JavaScript or HTML) code into a normal website. When other users browse the web, the website injected with the malicious code will automatically perform certain malicious purposes, such as importing other web pages and stealing user information.
B. Protection Products and Measures
As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must implement multi-layered information security protection to mitigate risks. Key security solutions include:
- Blocking unauthorized websites or software launches through network firewalls.
- Installing anti-ransomware software and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to counter cyberattacks.
- Establishing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to conceal digital footprints and enhance data privacy.
However, preventive measures alone are not enough. Proactive vulnerability assessment is essential to detect and address system weaknesses such as DDoS attacks, zero-day vulnerabilities, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. Regular vulnerability scanning and risk assessments help businesses identify security gaps and apply timely fixes to strengthen their defense.
Beyond technical defenses, businesses should obtain globally recognized information security certifications to validate their security measures. Certifications such as:
- ISO 27001 (International Standard for Information Security Management)
- SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls 2)
- GDPR Compliance (General Data Protection Regulation by the European Union)
These certifications demonstrate a commitment to data protection, compliance, and cybersecurity best practices, building trust with clients and stakeholders. Turing Certs has successfully obtained three major compliance certifications, ensuring the highest security standards for digital credentials.
One of the most fundamental security measures is encrypting cloud storage folders that manage sensitive data and credentials. Turing Certs provides encrypted digital certificates, ensuring secure credential management and safeguarding all critical information from potential cyber threats.
By implementing robust security solutions and obtaining international certifications, businesses can enhance data protection, prevent cyberattacks, and establish a trusted digital environment.
V. Turing Certs, the best solution to information security issues!
Turing Space is a TrustTech startup founded by Jeff Hu in 2020, dedicating to addressing the complexity of certifications among industries worldwide. We build up a borderless digital trust network with blockchain technology, advancing global digital transformation, aiming to become the cornerstone of international trust transmission.
Through Turing Certs, you can gain a variety of e-document and information security services:
✅ Large-quantity, quick credential creation and issuance
✅ Sign digital credentials
✅ Effectively manage digital credentials
✅ One-stop rental management with reasonable prices
✅ Verifiable information and immutable blockchain records
✅ Strictly verified digital credentials for enhanced information security
✅ Provide real-person customer service support so that even novices in digital tools can adapt quickly
![]() Media Contact|[email protected]
Media Contact|[email protected]